Penile Prosthesis
Penile implants are the last resort for severe Erectile Dysfunction, they are medical devices designed to help men with severe erectile dysfunction achieve an erection. They are considered a last resort when all other conservative treatment options, such as oral medications, penile injections, or vacuum erection devices, have been tried and proven unsuccessful. Common indications include organic ED, for instance, due to diabetes or vascular diseases, Peyronie’s disease, and traumatic injuries.

Semirigid Prostheses ????????????
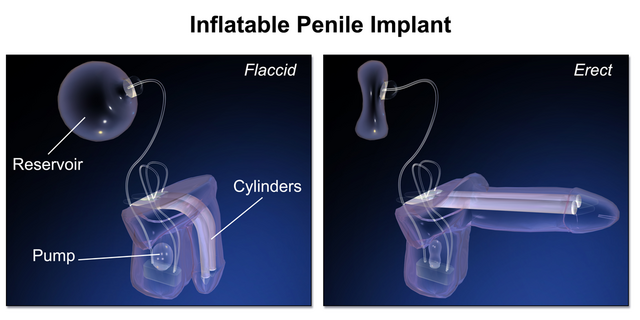
Hydraulic Prosthesis
Types of Penile Implants
Semirigid Prostheses
Structure: The semirigid prostheses are the flexible yet rigid rods implanted in corpora cavernosa or the erectile bodies.
Function: The penis always stays partially erected and may be moved manually from one position to another as necessary.
Advantages:
- Less invasive surgery with fewer complications.
- Relatively less expensive than hydraulic prostheses.
- Fewer mechanical breakages, since they have no moving parts.
Disadvantages: - Always semi-rigid may be obvious, could raise cosmetic issues.
- Not as natural in appearance as hydraulic models.
Hydraulic Prostheses
Structure: Hydraulic prostheses consist of three key parts:
- Cylinders implanted into the corpora cavernosa.
- A pump, usually placed in the scrotum.
- A fluid reservoir, usually placed in the lower abdomen.
Function: Fluid from the reservoir is transferred into the cylinders by squeezing the pump. The release mechanism returns fluid back to the reservoir and allows the penis to return to a flaccid state.
Advantages: - Provides a very natural look and feel in both flaccid and erect states.
- Fully implanted means the prosthesis is entirely concealed.
- Advantages include high satisfaction rates for patients and their partners.
Disadvantages: - It is a more complex surgery with a higher complication rate.
- More expensive compared to semirigid prostheses.
- Though very rare, mechanical failures can occur.
By understanding these features of each type, both the patient and healthcare provider can make appropriate choices based on individual needs and preferences.
Conclusion Penile implants are a very effective, permanent solution for men with severe ED when all other treatments have failed. They offer reliable erections and improved quality of life, but are irreversible and thus need to be weighed carefully. Consulting a specialist is essential to evaluate if this final option is the right choice.


