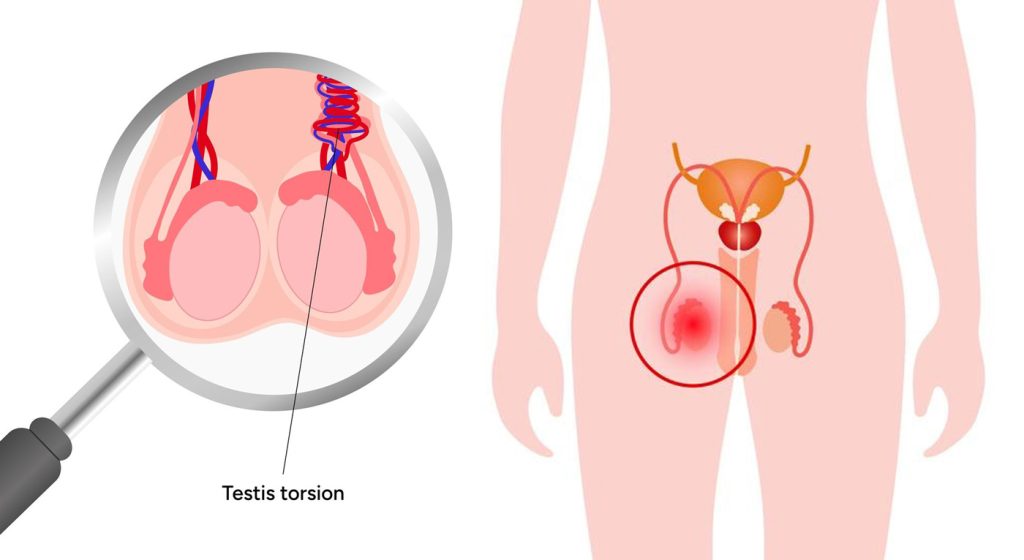
Testicular torsion is the act of the testicle wrapping around its blood supply line. It quickly cuts off the blood supply and is considered a serious emergency. When left unattended, permanent damage to the testicle occurs, so it’s important to recognize the signs and seek help immediately
Why Does Testicular Torsion Happen?
Two essential causes are there:
Spontaneous Torsion (Ideopathic): This is the most common type and occurs spontaneously, usually due to a problem in testicular development. Some men are born without a structure holding the testicle in place so that it can move more than it should; this could cause the testicle to twist around on itself. About half of the time, these cases occur at night during sleep, and sometimes it can take place in the course of physical activity or sports. This condition occurs more often in infants, teenagers and young adults; the left testis is involved more than the right.
Trauma: Less commonly, testicular torsion results from trauma to the scrotum or testicles.
Types and Degrees:
Testicular torsion can vary in degree from partial to complete, according to the extent to which the testicle is twisted:
In partial torsion, the outflow of blood from the testicle gets blocked while the arterial inflow remains intact, it causes swelling and can eventually completely cut down the supply of blood.
Complete Torsion: In this form, blood supply gets completely blocked and the testicle will die shortly due to lack of oxygen.
Symptoms:
As a parent, it’s important to know the warning signs of testicular torsion, especially in young children who may not be able to fully explain what they’re feeling. The major symptom of testicular torsion is sudden and severe pain in one of the testicles. This pain can radiate into the groin or lower abdominal region. Other symptoms and signs that might have accompanying features include:
• It is a high-riding testicle
• Swelling and redness of the scrotum
• Nausea or vomiting
• Older children may say the pain spreads to their lower abdomen or groin
• The testicle may feel like it is lying horizontally, rather than in its normal vertical position.
Sometimes, the patient experience mild pain that resolves by itself. This happens when the testicle partially twists up and then the torsion unwinds by itself. However, this is just a warning sign that shouldn’t be ignored.
Diagnosis and treatment:
If you suspect that you are or your child is experiencing testicular tortion, seek medical help immediately. Often a doctor can diagnose the torsion with a physical exam and the symptoms. Sometimes an ultrasound is gotten to confirm blood is still going to the testicle.
Rapid treatment is essential because, ideally, the testicle should be untwisted within 4-6 hours to avoid permanent damage. Sometimes, a manually untwist of the testicle by an experienced urologist is possible, but generally, immidiate surgery is the best option. This means that it can be untwisted and then stitched to the side so as not to torsion again. Usually, the other testicle is also similarly fixed to prevent future twisting later on. If reperfusion is delayed, the testis may incur irreversible damage, requiring a romoval of the testicle.
Why Time Matters:
The longer the testicle goes without blood, the greater the risk for permanent injury. After about 6 hours, the likelihood of saving the testicle decreases considerably, so time is of the essence. If treated early, the testicle can be saved and complications averted in the future.
Conclusion:
Testicular torsion is a real medical emergency. Knowing the symptoms—sudden pain and swelling—can help you act fast and protect your health. If you suspect torsion, never wait or put off going to the doctor’s clinic or to the next hospital since it might contribute to serious, long-term damage.