Uruinary Stones
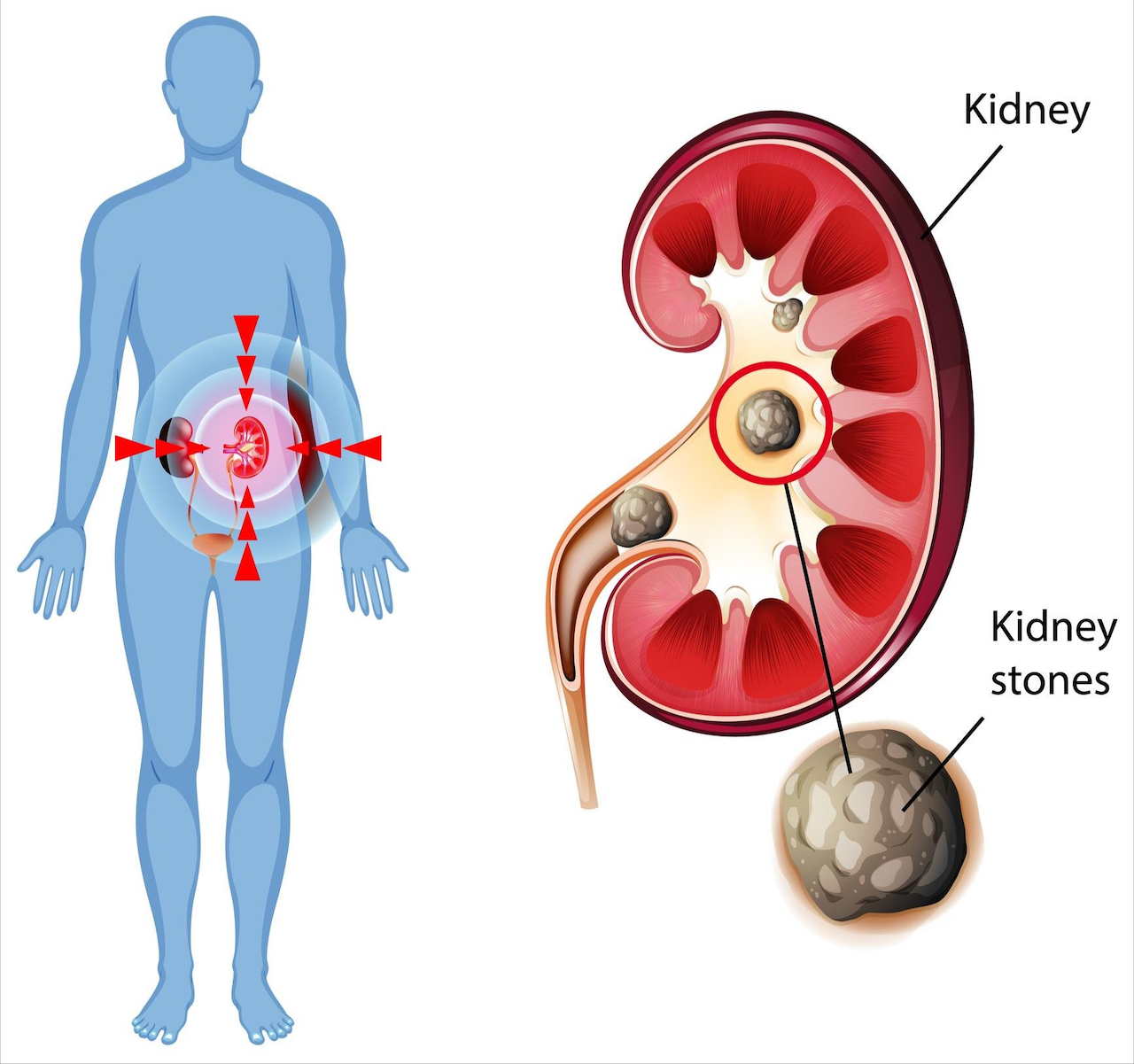
Urinary stones can affect any part of the urinary tract, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Causative factors are usually multifactorial. They include diet and hydration habits, metabolic disorders, and recurrent urinary tract infections caused by flow obstruction from prostatic hyperplasia and urine acidity.
Kidney stones generally are asymptomatic even if they are large, so are discovered incidentally during routine checkups. However, it can become symptomatic at times, leading to some mild flank pain.
When the stones shift into the ureter, they may trigger colic symptoms. These are unprovoked, intense, wave-like pains in the side that can radiate to the lower abdomen, groin, or testicles. Other symptoms may include urinary retention or extremely frequent urination, often painful. In such cases, urgent treatment is necessary.
The diagnosis is made from clinical symptoms, particularly pain; urine analysis for blood and stone components; ultrasound examination of the urinary tract; and CT scan. Treatment follows, depending on the size and location of the stones.
Conservative Medical Treatment
Pain relief, promoting the stones’ natural passage, and lowering the chance of new stones forming are the three main objectives of medical therapy. Acute symptoms are often treated with painkillers like diclofenac or ibuprofen. In certain situations, drugs can help relax the urinary tract’s muscles, which facilitates the passage of smaller stones.
Depending on the kind of stone, some drugs can also alter the urine’s chemical makeup, which lowers the risk of developing new stones. These could include, among other things, allopurinol or potassium citrate.
The size, location, and kind of stone all influence the best course of treatment. We are pleased to provide you with individualized guidance and create a treatment program that meets your needs.


Ureterorenoscopy (URS, RIRS)
Technological improvements in ureteroscopy have been quite significant over the last years, making this procedure much more refined and less invasive. With the help of equipment having rapidly decreasing diameters, complemented by specialized grasping forceps and laser lithotripsy, it is now possible to treat stones rapidly and safely.
A special optical instrument, either rigid or flexible, with a diameter ranging from 2 to 4 mm, depending on the size of the working channel, is passed under visual control through the urethra and bladder and then advanced into the ureter. Sometimes, the opening to the ureter needs dilation, and with X-ray guidance, the procedure can be monitored effectively.
Local injection of a contrast agent during ureteroscopy is very useful in visualizing the ureteral pathway and detecting obstructions. In instances where the path of the ureter is quite tortuous, a guidewire or very thin catheter may be passed through the working channel for easier guidance of the instrument. Ureteroscopy is primarily used for stone removal, where the stone is fragmented under direct vision. This may be done with specialized stone probes like mechanical-pneumatic, electromagnetic, electrohydraulic, ultrasound, or laser. The fragmented pieces are either naturally flushed out or extracted with the help of forceps or a retrieval basket.
After the procedure, a ureteral stent is commonly placed to prevent swelling of the ureter and its opening. This JJ or Double-J catheter needs to be removed after some time. If there is impaired bladder emptying, a urethral catheter can also be placed.
PCNL
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL or PNL) is an endoscopic procedure that is used as a minimally invasive surgery for the removal of large kidney stones.
Uses of PCNL in the treatment of nephrolithiasis include kidney stones larger than 1.5 cm, lower calyx stones over 10 mm, kidney stones that are resistant to treatment after extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), and calyceal stones with calyceal neck stenosis. Technological advances in miniaturization, such as Mini-PNL, have reduced the morbidity associated with PCNL, expanding its indications instead of ESWL.
PCNL depends very heavily on technical advances in equipment and the expertise of the surgeon for good results with fewer complications.
The kidney stone is punctured through the skin from outside, under the guidance of ultrasound and X-ray, and then fragmented under videoendoscopic vision using a laser before suctioning.
During this operation, an optical device called a nephroscope, about 4 to 9 mm in diameter, is introduced into the kidney through an access channel created. When stones are visible, the surgeon will break them with a laser. The fragments are either flushed out, suctioned, or retrieved by forceps and a retrieval basket. X-ray fluoroscopy is used intraoperatively to guide the procedure and ensure the kidney is as stone-free as possible. A temporary nephrostomy catheter is placed inside the renal collecting system and used to drain urine into a collection bag.

ESWL
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy (ESWL) is a urologic technique developed in Germany in 1982 that enables the fragmentation of urinary stones through shock waves. It is a noninvasive treatment where shock waves generated outside the body are used to break down stones into fragments small enough to pass naturally through the urinary system.
ESWL is mainly indicated for small to medium renal calculi and proximal ureteral stones. After stone fragmentation, small residual fragments usually remain in the kidney or ureter. Adequate hydration is essential to help flush out these fragments. These fragments may be excreted several days or up to several weeks after the procedure, depending on their initial size and location. Regular urological check-ups should also be conducted during this period. In the event of pain or fever, immediate urological evaluation is necessary.
In some cases an additional DJ Stenting maybe necessary to avoid renal colic after the procedure.
We Have Great Answers
Ask Us Anything
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.


